
If you work for an employer, your employer deducts the income tax from each of your paychecks. Indeed, both governments of the federal government and most collect tax on income the year, not just April 15 (April 18 for fiscal year 2015).
Every January or early February, you should receive a W-2 form from your employer that lists exactly how much money you made last year and how he went to taxes.
W-2 form is called feedback because it informs many major parties about your income and taxes paid for the year:
- federal
- your state (and city and local) government
- and you
form W-2 is one of those forms that you, the taxpayer, not having to fill !; your employer provides all the information on the form. In fact, your employer owes you, the IRS and your state's W-2 January 31 letter or face a penalty
Note :. You are required to attach your copy of the W-2 to your return. If you e-file using TaxAct, your W-2 information is sent with your return. However, if you file your tax return by mail, you must include a copy with your return.
The anatomy of W-2
W-2 form is very useful when you file your tax return Form 1040.
box number 1 contains your gross pay, tips and other compensation for the year. Boxes 2 and 17 tell you how much money was retained in federal tax and state, respectively, for the year.
The box 1 number, your income is reported on line 7 of your Form 1040. Federal taxes withheld in box 2 is reported on line 62 of your 1040
(Click here or on the W-2 picture form Instructions staff below to see a larger version)
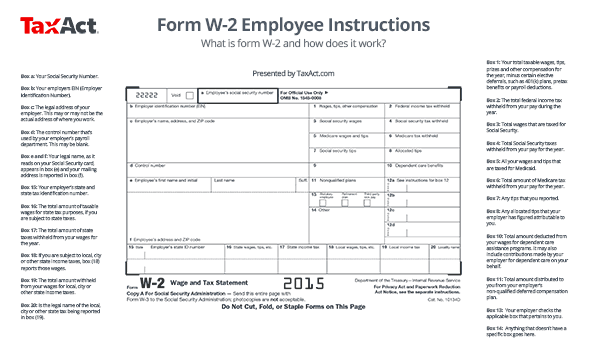
here is a detailed look each box of W-2
from boxes on the left:
box has: Reports your social security number. Make sure it is correct. Incorrect SSN may delay the processing of your tax return
Box b :. EIN (Employer Identification Number) from your employer is reported in box b. An EIN is a nine-digit number assigned to your employer by the IRS and used to identify tax accounts of employers
Box c :. Reports of the legal address of your employer. This may or may not be the actual address of where you work, depending on whether your employer has several offices with a corporate website
Box d :. Reports control number used by the payroll department of your employer. This may or may not be empty
Box e and f :. Your legal name, as it reads on your Social Security card, e appears in the box and mailing address is reported in the box Double-check both F are correct. If this information is incorrect, it may delay the processing of your return
Here's a closer look of the boxes on the right :.
Box 1 :. Displays your total taxable wages, tips, price and other compensation for the year minus certain elective deferrals, such as 401 (k) plans, benefits before taxes and payroll deductions
Box 2: total tax reports federal income withheld from your pay during the year. This amount is based on the number of exemptions depending on your form W-4 . If you prefer to keep more money in your paycheck each week, you'll want to adjust your form W-4 for the following year
Box 3: . Displays your total wages are taxed for Social Security
Box 4 :. total Social Security taxes on your earnings for the year. Unlike the federal income tax, social security taxes are calculated on the basis of a flat rate of 6.2%
Box 5: .. This tells all your wages and tips that are taxed for Medicaid
Box 6: the total amount of Medicare tax withheld from your pay for the year. Just as social security taxes, Medicare taxes are figured on a fixed rate, which is 1.45%
Box 7: .. This shows you tips declared
Box 8: This shows all tips attributed that your employer has figured attributable to you. They are treated as income
Box 9 :. This is empty, that requirement has expired. He is currently being removed from the W-2 form
Box 10 :. Reports the total amount deducted from your paycheck for dependents assistance programs. It may also include contributions from your employer for dependents on your behalf
Box 11: .. Reports of the total amount distributed to you non-qualified deferred compensation plan of your employer
Box 12: Reports of several different types of compensation and benefits. It will indicate a code letter or a double followed by a dollar amount. Here's what those codes mean:
A - Uncollected Social Security or RRTA tax advice
B - Uncollected Medicare tax on tips (but not additional tax health insurance)
C - taxable cost of group-term life insurance over $ 50,000 (included in your salary in boxes 1, 3 and 5)
D - elective deferrals to a 401 (k) Plan or species deferred arrangement (including a sIMPLE 401 (k) arrangement)
E - elective deferrals under a section 403 (b) a salary reduction agreement
F - elective deferrals under a section 408 (k) (6) pay cut in September
G - elective deferrals and employer contributions (including non-elective deferrals) to Article 457 (b) deferred compensation plan
H - elective deferrals to a 501 (c) (18) (D) organization plan tax exempt
J - sickness benefit nontaxable
K - 20% excise tax on excess parachute payments gold
L - corroborated business expense reimbursements employees
M - Uncollected social security or RRTA tax on taxable cost of group-term life insurance over $ 50,000 (former employees only)
N - Uncollected Medicare tax on taxable cost of group-term life insurance over $ 50,000 (but not additional tax health insurance) (former employees only)
P - EXCLUDED move repayments fees paid directly to employees
Q - nontaxable combat pay
R - Employer contributions to an Archer MSA
s - contributions from employee pay cut under a section 408 (p) Simple Plan
T - adoption benefits
V - income from the exercise of the option (s) of non-statutory actions
W - employers' contributions (including contributions by employees through a cafeteria plan) on the health savings account of an employee (HSA)
Y - deferrals under a section 409A nonqualified deferred compensation plan
Z - income pursuant to a nonqualified deferred compensation plan that does not meet 409A
AA - designated Roth contributions to a 401 (k) plan
BB - Roth contributions designated under section 403 (b) plan
DC - Hiring salaries and advice provided (2010 only)
DD - Cost of protection offered by the employer health
EE - designated Roth contributions under a governmental section 457 (b) plan
box 13: Your employer tick applicable box that relates to you as an employee. statutory employee means employees whose earnings are subject to Social Security and Medicare, but not the withholding tax on federal income. Pension Plan means that you participated in your employer's pension plan during the year. third party sick pay means that you receive sickness benefits under the third of your employer's insurance policy
Box 14 :. Reports of all that doesn 't have zero specific box elsewhere on the W-2 in box 14.
Box 15: Includes the state and the state of the tax identification number of your employer
Box 16: Indicates the total amount of taxable wages for tax purposes of the state, if you are subject to the income tax of the state
Box 17 :. Displays the total amount of state taxes withheld from your salary for the year
Box 18: .. If you are subject to local, town or other taxes on income of the state, box 18 reports wages
box 19: reports the total amount withheld from your wages for local, city or other taxes the income of the state
Box 20 :. is the legal name of the local, city or other state tax being in box 19.
All information on your W-2 form to determine if you need more taxes or if you receive a tax refund.
If you find that you regularly need large amounts in April, you can adjust your deductions. This is done using the W-4 form.
You've probably filled out a W-4 to your first day at work. Talk to your human resources department about lowering your number of exemptions or the addition of a deduction at source elective
If you have the opposite problem -. A big refund each April -. So you retain too much of each paycheck
Make sure your load is accurately entered.
Not every taxpayer receives a W-2.
freelancers and independent contractors receive Form 1099-MISC, another kind of feedback for "non-employee compensation."
There are other types of returns for 1099 income investment such as capital gains, dividends and interest, which count as income.

0 Komentar